As energy costs continue to rise and the effects of climate change become more evident, many homeowners are asking a crucial question: Is residential solar power worth it? Investing in solar energy can be a significant financial commitment, but it also promises long-term savings, environmental benefits, and energy
independence. This article explores the real value of residential solar power, its pros and cons, and how to determine if it’s the right choice for your home.
What Is Residential Solar Power?
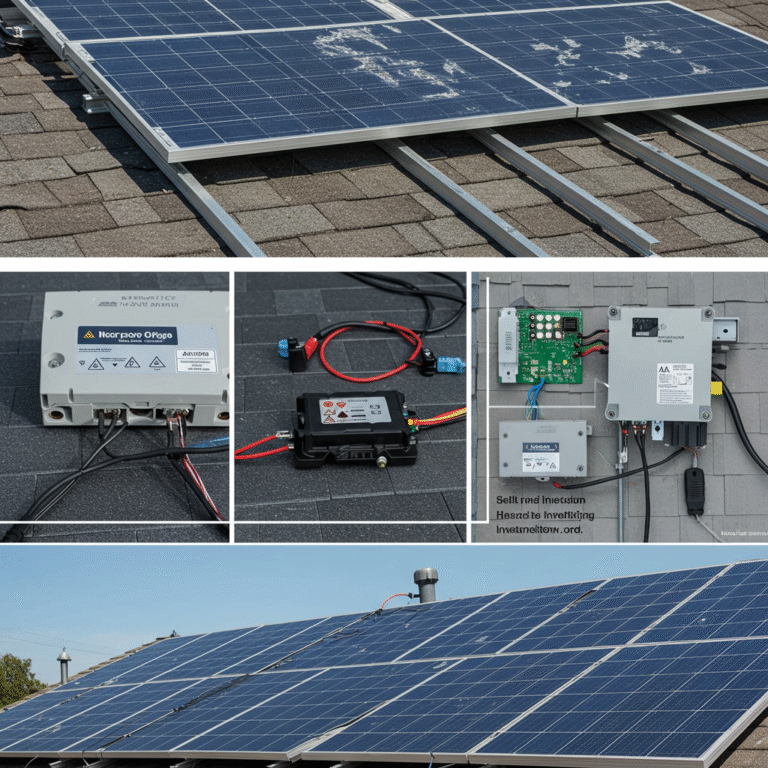
Residential solar power involves installing photovoltaic (PV) panels on the roof or property of a home to convert sunlight into electricity. This electricity can power household appliances, lighting, heating, and cooling systems. Excess energy can often be stored in batteries or fed back into the grid, depending on local regulations and net metering policies.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
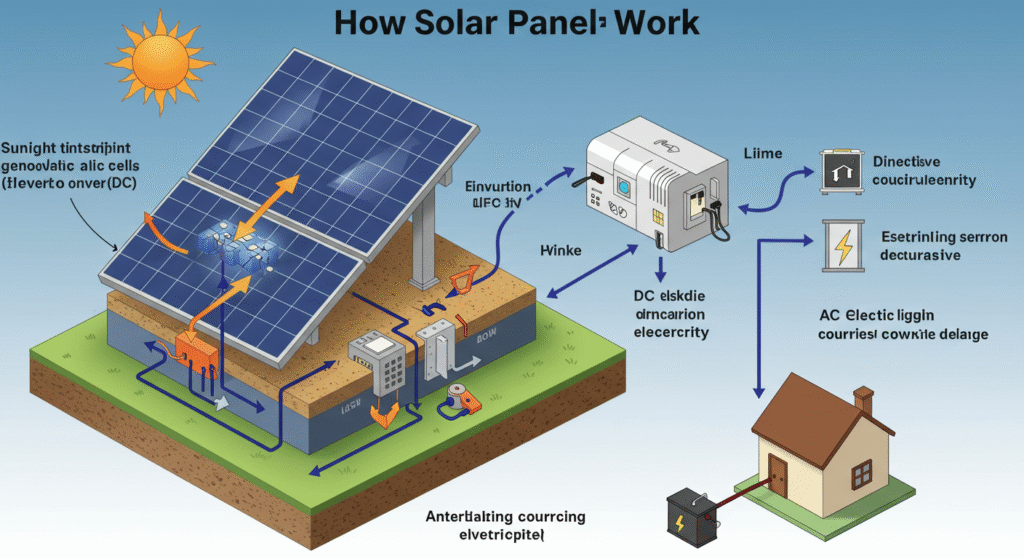
Solar panels are made up of many solar cells, typically constructed from silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it excites electrons, creating an electric current. This direct current (DC) is converted to alternating current (AC) using an inverter, making it usable in your home.
The Cost of Installing Solar Panels
The upfront cost of a residential solar power system varies based on several factors:
- System Size: Larger systems produce more electricity but cost more.
- Location: Installation and permitting fees vary by region.
- Roof Type and Condition: Complex or damaged roofs may increase labor costs.
- Battery Storage: Optional battery storage systems increase overall cost.
On average, the cost to install a solar system ranges from $15,000 to $30,000 before incentives. Federal and state tax credits, rebates, and solar incentives can significantly reduce this amount.
Financial Incentives and Tax Credits

Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
The federal government currently offers a 30% tax credit on the total cost of solar installation. This incentive is scheduled to phase out over the next few years, so acting soon can maximize your savings.
State and Local Incentives
Many states, counties, and utilities offer additional rebates or tax incentives, such as:
- Sales tax exemptions
- Property tax exemptions
- Performance-based incentives (PBIs)
- Net metering credits
Use the DSIRE database to find current solar incentives in your area.
How Much Can You Save with Residential Solar?
1. Monthly Utility Bills
Solar panels can drastically reduce or even eliminate your electricity bill. The average U.S. household saves $600 to $2,000 per year.
2. Return on Investment (ROI)
Most homeowners break even on their solar investment within 6 to 10 years, depending on electricity rates, system cost, and available incentives.
3. Long-Term Savings
Solar panels typically last 25–30 years, meaning you could enjoy 15–20 years of virtually free electricity after recouping your investment.
Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
- Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Decreases Dependence on Fossil Fuels
- Promotes Sustainable Energy Sources
- Lowers Water Usage in Energy Production
By switching to solar, the average homeowner offsets the equivalent of 100,000 pounds of carbon dioxide over 20 years.
Factors to Consider Before Installing Solar Panels
1. Roof Orientation and Shading
South-facing roofs with minimal shade provide the best solar exposure. Trees, chimneys, and nearby buildings can obstruct sunlight and lower system efficiency.
2. Home Energy Usage
Evaluate your current energy consumption. Higher usage generally means greater savings.
3. Local Climate
Solar panels work even in cloudy weather, but sunnier climates naturally yield better performance.
4. Homeownership Duration
If you plan to stay in your home long-term, the benefits of solar are more likely to outweigh the upfront cost.
Financing Options for Residential Solar Power
1. Cash Purchase
- Highest upfront cost
- Maximum long-term savings and tax benefits
2. Solar Loans
- Pay in monthly installments
- Eligible for tax incentives
- May include interest payments
3. Solar Leases & Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
- Little or no upfront cost
- Lower monthly savings
- No system ownership, so limited benefits
Pros and Cons of Residential Solar Power
Pros:
- Significant energy cost savings
- Increase in property value
- Environmentally friendly
- Low maintenance
Cons:
- High initial investment
- Effectiveness depends on location
- May require roof upgrades
- Limited effectiveness in shaded areas
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Is residential solar power worth the investment? A: For many homeowners, yes. If you have high electricity bills, good sun exposure, and plan to stay in your home long-term, solar can offer excellent ROI and savings.
Q2. How long do solar panels last? A: Most solar panels last between 25–30 years, with gradual efficiency loss over time.
Q3. Do solar panels work during cloudy days or at night? A: Yes, they work during cloudy days but with reduced efficiency. At night, solar panels do not produce electricity, but battery storage or grid connection can cover usage.
Q4. Will solar panels increase my home value? A: Studies show that homes with solar systems sell faster and for more money than non-solar homes.
Q5. What maintenance do solar panels require? A: Minimal maintenance is required. Occasional cleaning and annual inspections are usually sufficient.
Conclusion
Residential solar power is a smart investment for many homeowners looking to reduce electricity bills, increase energy independence, and minimize their environmental impact. While the upfront cost can be high, government incentives and long-term savings make it a compelling option.
Final Thought
If you’re considering making the switch to solar, start by evaluating your energy usage, home orientation, and available incentives in your area. In many cases, solar power not only pays for itself but also adds value to your home and contributes to a cleaner planet. The question isn’t just “Is it worth it?” — it’s “Can you afford not to?”